
Javier Blas, Bloomberg News
LONDON
EnergiesNet.com 04 14 2024
Recently, I asked the head of a state-owned oil company in the Middle East what price OPEC+ is aiming for. Laughing, he replied: $99.99 a barrel, and not a single cent higher. Even following Iran’s missile attack on Israel, there’s a good chance the cartel can keep crude prices below the triple-digit barrier.
My interlocutor was intentionally flippant, but directionally, his assessment sounds about right. Yet, on any given day, achieving oil prices that are neither too hot nor too cold is extremely difficult. The geopolitics of the Middle East only confuses the calculus and makes it almost impossible to reach the fabled goldilocks level.
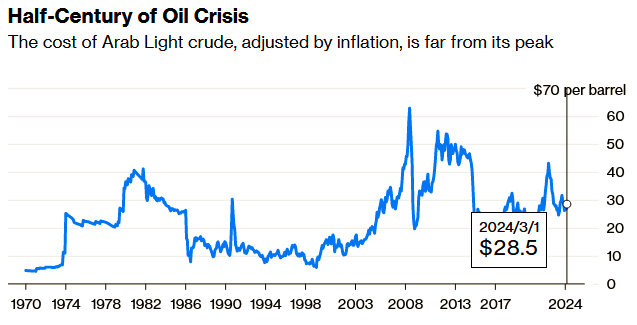
Inflation adjusted using US urban consumer price index 1983=100
The situation is fluid, and for the oil market, everything depends now on how Israel’s response and the chance of a cycle of escalation. Still, we can draw a few tentative conclusions:
1) From a purely physical standpoint, nothing has changed in the world of oil. Middle Eastern crude is flowing into the global economy unimpeded, and the Strait of Hormuz, the world’s most important energy chokepoint, remains open to shipping. Put simply: there’s no oil shortage.
2) The risk of a future disruption has increased. It would be naïve to say the Middle East looks today exactly as it did last week; a lot did change. I don’t think it was a purely symbolic attack. Even though telegraphed well in advance, Iran launched about 170 drones, 30 cruise missiles and 120 ballistic missiles, with the clear aim of overwhelming Israel’s defences. The options market, via deep out-of-the-money call contracts, should reflect the higher risks.
3) Iran appears to have aimed for an escalation to-deescalate, rather than opening the first chapter of a regional war.Even well before the drones and missiles reached Israel, Tehran indicated the attack was a one-off “legitimate defense” after the Israeli bombing of its embassy in Syria: “The matter can be deemed concluded.” If Israel considers that its response, bringing America and several Arab nations alongside to neutralize almost all the incoming bombs, was akin to a strategic victory, then the region returns to its precarious status quo. If so, headline oil prices don’t need to rally. Instead, the risk willbe reflected better via the options market.
4) Putting aside geopolitics, oil supply and demand fundamentals look healthy. Even the most bearish forecast for oil demand suggests consumption growth in 2024 will match the historical annual average of 1.2 million barrels a day. The bullish forecasts are for much higher growth, in the 1.5-to-1.9 million barrels a day range. On the supply side, a series of glitches have reduced production this year, particularly of US shale oil. As a result, global oil inventories, which typically increase in the first half of the year, have remained unchanged. Unless OPEC+ increases production soon, stockpiles will drop in the second half of the year.
5) OPEC+ is keeping the market tight. Despite oil prices well above $80, it decided in late March to roll over its first-quarter output cuts into the second quarter. My expectation is that the group will open the taps at its next meeting, scheduled for June 1. In its last monthly oil report, the cartel noted on April 11 that the “robust oil demand outlook for the summer warrants careful market monitoring” – the kind of preparatory language ahead of an output hike.
6) How OPEC+ increases production would be as important as the hike itself. I expect the group to hike output slowly, leaving its options open. Rather than pre-announcing a series of production increases, it could instead opt to call monthly meetings, keeping the market guessing whether it would add enough crude.
7) Unless Israel and Iran engage in tit-for-tat attacks that disrupt oil flows, OPEC+ has more than enough spare production capacity to control a price rally. Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, and Iraq are keeping about 5 million barrels of day out of the market – equal to about 5% of the world’s demand, and more than what Iran itself produces.
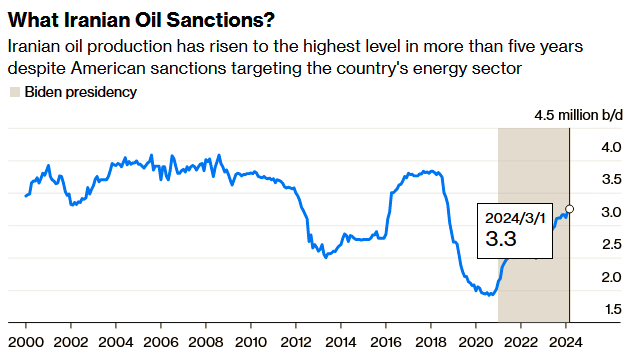
8) Barring a regional war, the biggest oil supply risk is political. President Joe Biden has promised a “diplomatic” response to the Iranian attacks. Since he was inaugurated in 2021, Biden has all but allowed Iran to increase its oil output, relaxing the enforcement of US sanctions on Tehran. In March, Iranian oil output hit a five-year high of 3.25 million barrels a day, up from 2.1 million in January 2021. If Biden resumes enforcing the sanctions, it could tighten the market significantly unless OPEC+ offsets the impact. I’m dubious Biden would take that course of action in an election year.
9) Russia stands to win. Thanks to a tight oil market, Moscow is already selling its crude at $75 a barrel, well above the Group of Seven cap of $60 a barrel. If Washington enforces sanctions against Iran, it could create space for Russia’s own sanctioned barrels to both win market share and achieve even higher prices. One of the reasons why the White House turned a blind eye to Iranian oil exports is because its priority was to hurt Russia. Higher Iranian production was the unsaid — and unrecognized — cost of that policy. Now Washington needs to reconsider what’s its biggest concern.
10) The risk that the White House would tap the country’s Strategic Petroleum Reserve later this year has increased notably. Even if half the size it was a decade ago, the stockpile of about 365 million barrels is still a formidable force. Biden can use the cover of rising tension in the Middle East to justify its use and try to push oil prices down toward $80 a barrel if OPEC+ decides it’s happy letting them rise to $99.99, or even beyond.
Javier Blas is a Bloomberg Opinion columnist covering energy and commodities. He is coauthor of “The World for Sale: Money, Power and the Traders Who Barter the Earth’s Resources.”
bloomberg.com 04 14 2024
EnergiesNet Latam News











