
Kevin Crowley, Paul Takahashi and Sheela Tobben, Bloomberg News
HOUSTON/NEW YORK
EnergiesNet.com 05 27 2022
In a world crying out for more oil, a dusty stretch of West Texas and southeastern New Mexico is one of the only places that can deliver. But even with crude above $100 a barrel, producers in the Permian and other US shale basins are riding the brakes.
For most of the past decade, the Permian was an unstoppable drilling machine. Its vast, low-cost reserves helped transform the US into the world’s swing oil supplier, primed to turbocharge output as soon as prices soared or to halt when they collapsed. Because shale producers amassed a backlog of wells that could be tapped in just a few weeks, a crude rally was sure to incite a fracking frenzy that would help replenish global stockpiles and cool off prices.
But not this time.
After Russia invaded Ukraine in late February, crude prices surged to a 13-year high. Gasoline is above $4 a gallon in every US state for the first time. Jet fuel in New York spiked to a record last month. Yet shale explorers show no sign of riding to the rescue. Their business model has fundamentally changed, reshaped by pressure to curb growth and divert cash to investors with dividends and buybacks. Inflation is also taking a toll. US oil output this year is expected to expand by less than half the amount it did in 2018, when crude traded around $65. That means more pain for consumers, with JPMorgan Chase & Co. predicting US gasoline at $6.20 a gallon by August.
“The US oil and gas supply system remains very potent, but at any given price, growth will be smaller and slower,” said Raoul LeBlanc, vice president for North American upstream oil and gas at S&P Global. “Without the subsidy that shale shareholders provided, consumers can expect to pay higher prices.”
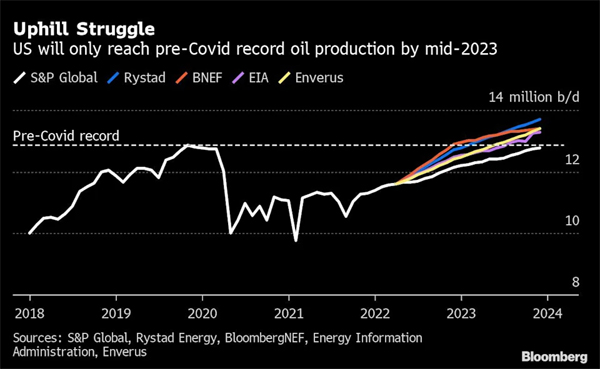
The US will add about 900,000 barrels a day of oil production this year, according to the average of five major forecasters: S&P Global, Rystad Energy, BloombergNEF, Enverus and the US Energy Information Administration. That compares with 1.9 million a day in 2018. This year’s growth was planned before Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, and analysts only see a modest increase of about 800,000 barrels a day next year, which would finally bring US output to pre-pandemic levels. In the field, operators say forecasters’ current estimates may even be too optimistic. Several OPEC producers, meanwhile, are struggling to fill their output quotas, leaving the global crude market increasingly tight.
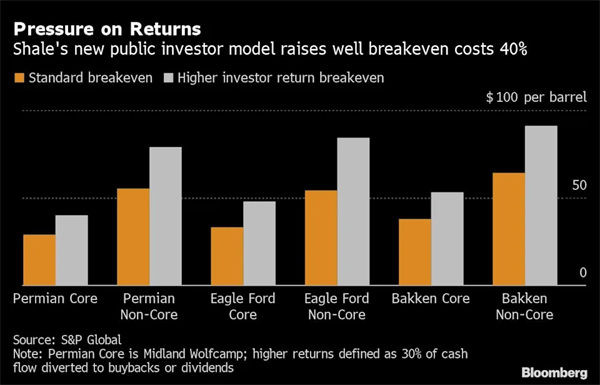
Wall Street isn’t the only source of shale’s growing pains. The global supply-chain crisis is particularly acute in the Permian Basin, which will make up 80% of this year’s US production growth, according to research and data firm Enverus.
Disruptions to equipment supplies mean if a company wants to increase production, it would now take a year or more between drilling to pumping oil, up from three to four months before the pandemic, Linhua Guan, CEO of Permian driller Surge Energy, said in an interview. Guan planned for 16% cost inflation this year and says that will increase next year. As a result, Surge expects a 12% annual production growth rate this year, down from 29% in the 12 months through the first quarter. Even so, Guan expected the U.S. subsidiary of China’s Shandong Xinchao Energy Co. will make record profits this year if prices remain elevated.
The cost of casing, a lining that helps to stabilize wells, is three times higher than usual and lead times to fill orders are much longer, said Dena Demboski, vice president of operations at Permian producer UpCurve Energy LLC. “Rig rates are higher than I’ve ever seen them” at more than $30,000 a day, she said. Pioneer Natural Resources Co., a major Permian driller, expects the cost of contracts for new rigs to rise as much as 40% next year.
America’s oil production increased by 7.05 million barrels a day from 2012 to 2019, adding new output equivalent to Iran and Iraq combined in just eight years. OPEC failed in its multiple attempts to sideline shale producers by allowing prices to crater. And yet U.S. shale now has little hope of replacing the estimated 2 million to 3 million barrels a day from Russia that are either shut-in or deemed untradeable because of sanctions.
“The Russian production supply gap is too big for shale to fill in alone,” said Al Salazar, senior vice president of Enverus. Oil field “constraints and producer discipline limit shale’s ability to cool prices” this year.
The jump in oil and gasoline prices has helped drive US inflation to the highest levels in decades, and it’s becoming increasingly clear that shale is no longer the silver bullet to counter skyrocketing crude prices. President Joe Biden appears to have abandoned public calls to encourage US drillers to boost production, a key focus for his administration earlier in this year. He’s now considering a meeting with Saudi Arabian Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman, according to people familiar with the matter.
“The Permian is going to be there to help,” Pioneer Natural Resources CEO Scott Sheffield said at Hart Energy’s DUG Permian conference in Texas last week. But “is that going to save the world? Not with what happened” in Ukraine, he said.
bloomberg.com 05 25 2022












